One of the 7 most overhyped tech buzzwords. How do they work? What problems do they solve and how can they be used? These days we have a lot of misconceptions about technologies in addition to a lot of concepts that can be difficult to grasp. In future blog posts, I want to dive into the fundamentals of blockchain, how that impacts the world and different industries. And will start with  definitions.
definitions.
Blockchain is a shared, distributed ledger that facilitates the process of recording transactions and tracking assets in a business network. An asset can be tangible a house, a car, cash, land, or intangible like intellectual property, such as patents, copyrights, or branding. Virtually anything of value can be tracked and traded on a blockchain network, reducing risk and cutting costs for all involved.
Most of us are probably familiar with cryptocurrency. Blockchain is used to track the transaction.
Enabling a new level of trust
The true innovation of blockchain is its ability to automate trust among the parties using it. Transactions are settled in a collectively fashion and recorded on a distributed ledger, which removes the need for an established third party to create a trusted relationship. Participants can directly use the blockchain as the source of truth instead of one another.
Like the name forebode, a blockchain is a chain of blocks. It contains information this technique was originally described in 1991 by a group of researchers and was originally intended to timestamp digital documents so that it’s not possible to backdate them. However, it went by mostly unused until it was adapted by its though she Nakamoto in 2009 to create a digital cryptocurrency.
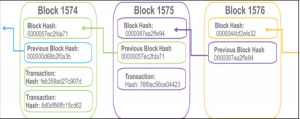
Bitcoin blockchain as a distributed ledger that is completely open to anyone they have an interest in the property. Once some data has been recorded inside a blockchain it becomes very difficult to change it. So how it works? Block contains some data the hash of the block and a hash of the previous block the data that is stored inside a block at the pain. Some types of blockchain the Bitcoin blockchain for example stores the details about a transaction here such as the sender-receiver and the number of coins also have hash you can compare a hash through a fingerprint that identifies a block and all of its contents and it’s always unique just like a fingerprint.
Once a block is created its hash is being calculated changing something inside the block will cause the hash to change. Another words hashes are very useful when you want to detect changes the blocks if the Fingerprints of a block changes it no longer is the same block the third element inside each block. The hashes of the previous block effectively create a chain of blocks and it’s this technique that makes a blockchain so secure.
Throughout history, trust instruments, such as minted coins, paper money, letters of credit, and banking systems, have emerged to interfere with the exchange of value and protect buyers and sellers. Important innovations, including telephone lines, credit card systems, the Internet, and mobile technologies have improved the convenience, speed, and efficiency of transactions while shrinking and sometimes virtually eliminating the distance between buyers and sellers. Blockchain aims to take it all to an even higher level of security, which none of these instruments and tools have had so far.
It was also noted that blockchain technology is a great fit for high-risk industries, including cannabis, gambling, and adult entertainment which can be an issue from financial services companies. These industries find it difficult to interact with the traditional financial system, and often experience long settlement times over traditional networks. Blockchain aims to cover this too.
Bibliography
Manav Gupata (2018). Blockchain for Dummies, from https://www.ibm.com/downloads/cas/D8O9VBAK



