In today’s digital world, cybersecurity is a top priority for organizations. One concept that has been gaining ground in this landscape is Zero Trust Security. In the past two years, adoption of this modern security framework has more than doubled. But what is it, and how does it work? Let’s dive in to find out.
What is Zero Trust Security?
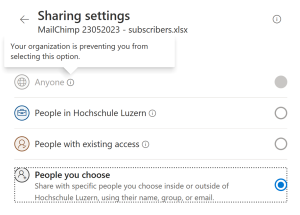
You have probably seen some changes recently while working on Excel, or Word and trying to share the document with someone else. And maybe, like I did you have copied the link like you used to do at home, and sent it to your colleague who, after 5 minutes of trying to click on the link and connect has sent you a message: “Sorry, I can’t access the document. Could you send it again?” Well, you are not the only one. This is a basic form of Zero Trust Security, a security model based on a strict identity verification process. The principle of “never trust, always verify” is at its core, which means no one inside or outside the network is automatically trusted. This strategy requires verification from anyone trying to access resources in a private network.
The Evolution of Zero Trust Security
The term Zero Trust was coined by John Kindervag, a former Forrester Research analyst, in 2010. It came as a revolutionary response to the traditional security models that operated on the outdated assumption that everything inside an organization’s network was safe.
According to the 2022 State of Zero-Trust Security report, 61% of organizations today have a Zero Trust initiative in place, and another 35% plan to implement one soon
The Zero Trust model acknowledges that threats can come from anywhere: external sources or insiders. It promotes a more rigorous approach to security.
“We discovered in our research that insider threats are not viewed as seriously as external threats, like a cyberattack. But when companies had an insider threat, in general, they were much more costly than external incidents. This was largely because the insider that is smart has the skills to hide the crime, for months, for years, sometimes forever.”
— Dr. Larry Ponemon, Chairman and Founder of the Ponemon Institute
The Principles of Zero Trust Security
- Verify Identity: Before granting access, the system confirms the identity of the user or device.
- Least-Privilege Access: Users are given the minimum levels of access or permissions needed to accomplish their tasks.
- Micro-Segmentation: Networks are divided into smaller zones to maintain separate access for separate parts of the network.
Benefits of Zero Trust Security
- Enhanced Security: By not automatically trusting anything, the chances of a security breach are substantially reduced.
- Protection Across Various Devices: It provides security not just for networks but for individual devices as well.
- Compliance: Many organizations find it easier to comply with regulatory requirements due to the rigorous controls in place.
In numbers, this represents:
- 50% decrease in IT and help desk calls
- 50% reduction in risk of data breaches
- 75% faster device setup for new users
- 1’000’000
Zero Trust reduces the cost of a data breach by about $1 million. - 1st priority
Adding layered security to secure work-from-anywhere models is the number one priority for IT professionals at SMEs in both 2021 and 2022.
Implementing Zero Trust Security
Implementation is a step-by-step process, often beginning with acquiring the right technology and expertise. Companies generally follow these steps:
- Identify Sensitive Data: Understand what kind of data you are handling and where it resides.
- Map the Transaction Flows: Have a clear understanding of how data moves through your organization.
- Build a Zero Trust Architecture: Develop a Zero Trust architecture that supports your data and transaction flows.
- Monitor Networks Continuously: Continuously monitor the network to detect any unusual patterns or behaviors that might signify a threat.
https://soundcloud.com/thibault-darbellay/what-is-zero-trust-security-a-beginners-guide



Very interesting blog post about cyber security. I really learnt a lot.